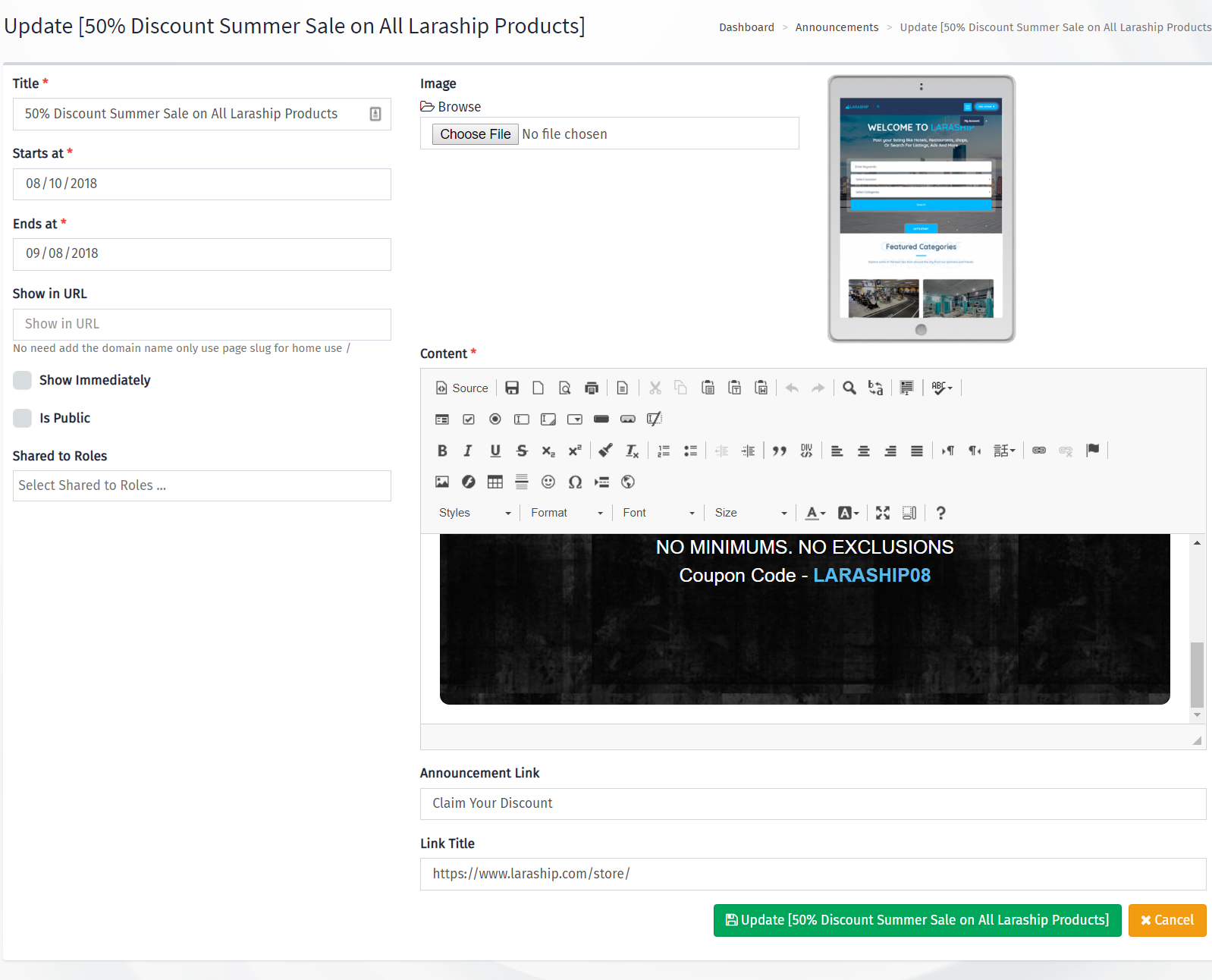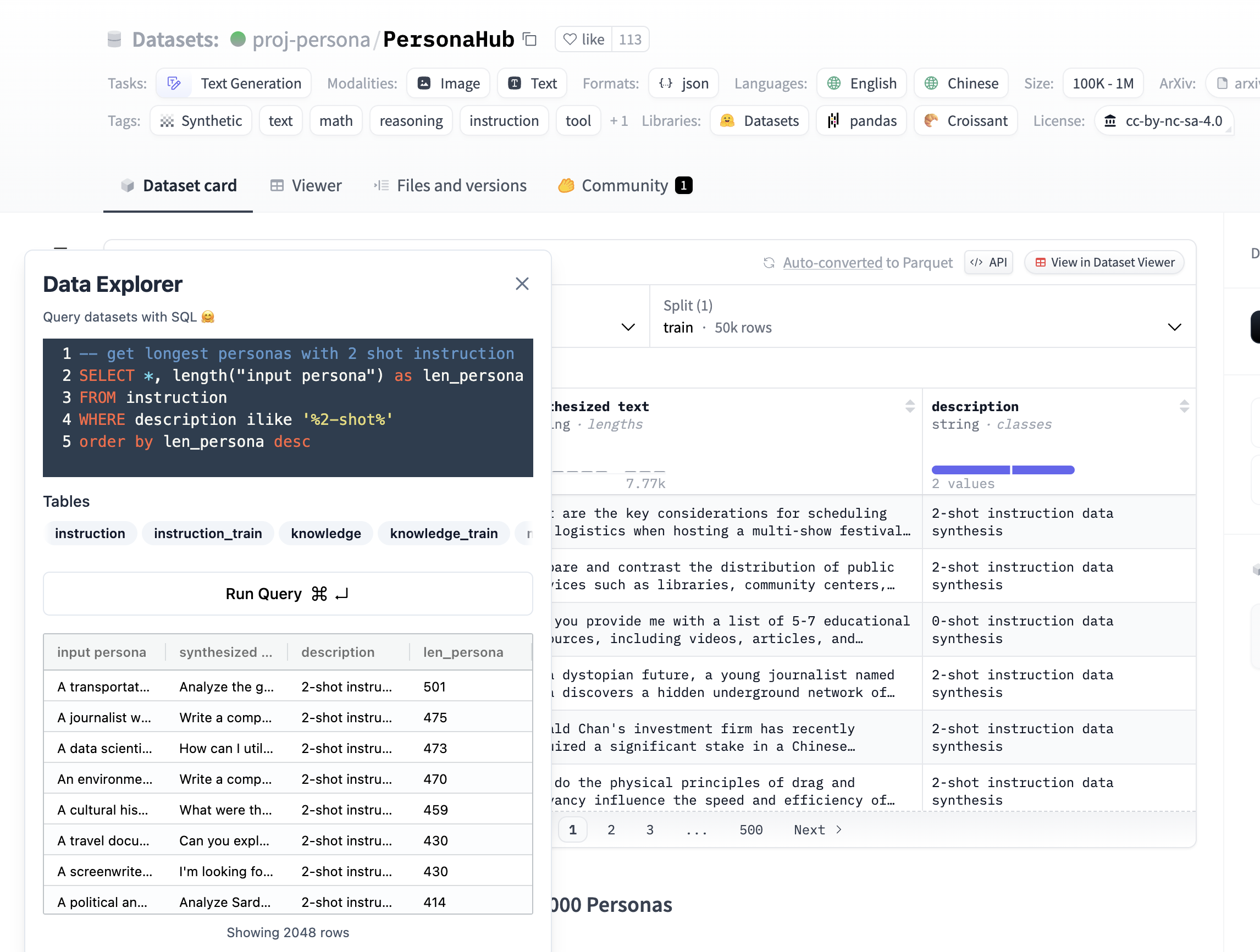

This feature has been archived since it is available natively in Hugging Face now. You can learn more about it here.
A Chrome Extension for exploring and query Hugging Face datasets with SQL.
- Download the latest release from the Releases page.
- Unzip the downloaded file.
- Open Google Chrome and navigate to
chrome://extensions/. - Enable “Developer mode” by toggling the switch in the top right corner.
- Click on “Load unpacked” button.
- Select the unzipped folder containing the extension files.
- The HF Data Explorer extension should now be installed and visible in your Chrome toolbar.
DuckDB WASM can only use ~ 4GB of memory (more like 3.4GB with duckdb memory limit). Since DuckDB WASM can’t spill extra data to disk like the other clients, it may not be able to perform very large or advanced queries. However, DuckDB WASM is still very fast, performant, and can work for most workloads.
This is a Plasmo extension project bootstrapped with plasmo init.
First, run the development server:
pnpm dev
# or
npm run devOpen your browser and load the appropriate development build. For example, if you are developing for the chrome browser, using manifest v3, use: build/chrome-mv3-dev.
You can start editing the popup by modifying popup.tsx. It should auto-update as you make changes. To add an options page, simply add a options.tsx file to the root of the project, with a react component default exported. Likewise to add a content page, add a content.ts file to the root of the project, importing some module and do some logic, then reload the extension on your browser.
For further guidance, visit our Documentation
Run the following:
pnpm build
# or
npm run buildThis should create a production bundle for your extension, ready to be zipped and published to the stores.
 https://github.com/cfahlgren1/hf-data-explorer
https://github.com/cfahlgren1/hf-data-explorer